Advantages
How to choose a privileged access management tool
Before we explain how to choose a privileged access management tool, let's take a look at the three operations required for privileged access management.
Privileged access management requires the company to properly manage who receives and uses privileged IDs. Basically, it is necessary to perform administrative operations in this order: privileged ID management (Level 1), privileged access granting (Level 2), and privileged access inspection (Level 3). First, let's review your current level of operations and decide what you want to achieve by installing a privileged access management tool and how much you want to manage. Then choose the product that is right for your company.

Do you have all the features you need? Make sure you can meet auditing requirements not just now, but for future issues.
Although there are many privileged access management tools already available, they have different features and functions and are hard to compare.
All privileged access management tools provide a variety of functions, but now, there are five capabilities that address the three operations required for privileged access management.
These five features can come all in one package, or you can pick the ones that fit your objectives and environment. Check to see which product works for you.

There are three types of privileged access management tools Make sure they can inspect privileged access, including remote and direct access.
There are three main types of privileged access management tool methods: Client-agent, gateway, and server-agent types. Each method differs in two ways: Access control (where the privileged access granting control happens) and log acquisition (where the logs are acquired and inspected). These differences are the pros and cons of privileged access management products.
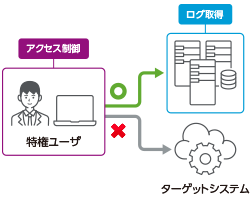
Client-agent type
- ●
- The access control is done by a client agent (nonresident program) deployed on the access source PC.
- ●
- Access logs are acquired directly from the target system.
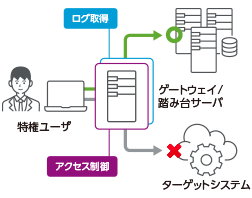
Gateway type
- ●
- Access control is done by the gateway.
- ●
- Only remote access logs that pass the gateway are acquired.
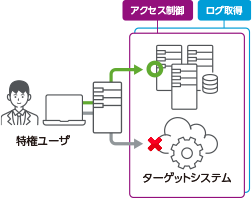
Server-agent type
- ●
- Access control is done on the server agent (resident program) deployed on the server to which it is connected.
- ●
- Logging is acquired on the target system.
The differences in the various methods determine the ease of deployment (impact range), access control, and thoroughness of log inspection (access and operation logs).
- ●
- Comparison of methods used by privileged access management tools
| Inspection Point | Client-Agent | Gateway | Server-agent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ease of deployment |
Requires installment of client agent (non-resident program) on the access source PC
Can be installed on a bastion server |
Fully agentless for easy deployment
Requires network configuration |
Requires the target system to install a server agent (resident program), which has a significant impact on the server Also has high deployment costs |
| Impact range | The access source PC / server | The entire network |
The entire target system
(applications, middleware, everything higher than the OS) |
| Access control |
Allows control of privileged access granting regardless of access paths |
Only allows control of communication through the gateway (direct or multi-stage access cannot be controlled) | Allows specific configurations |
| Access log inspection |
Can inspect everything, including remote and direct access |
Can only inspect remote access through the gateway | Can inspect all access including remote and direct access |
| Operation log records |
Records as video/text data from the access source, gateway, and server |
Records as video/text only data that passes through the gateway | The server agent records data as text |
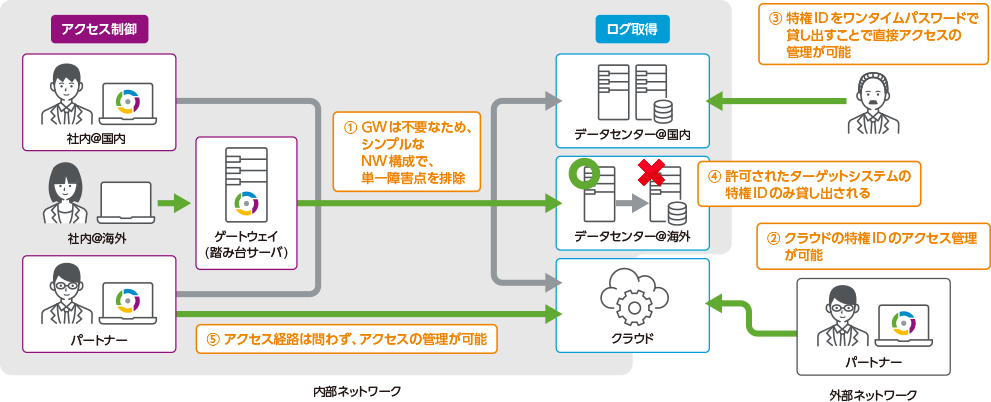
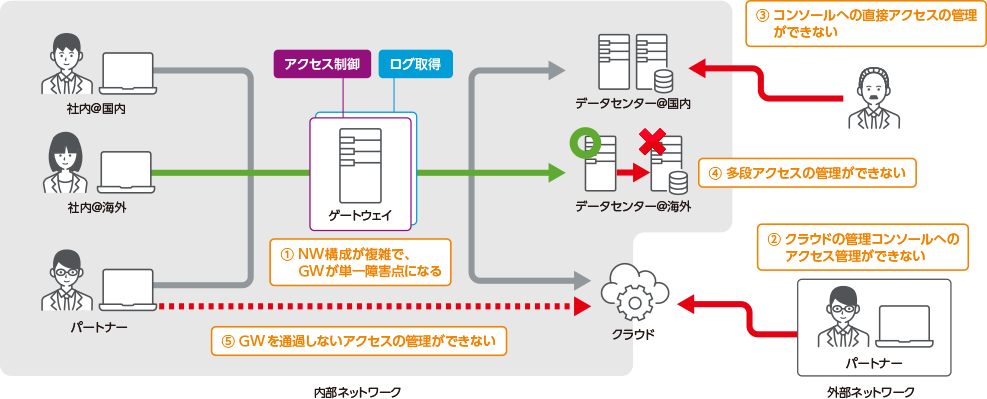
The five problems with gateway-type privileged access management tools
Gateway-type privileged access management tools adopt a method of establishing a gateway server between a privileged user and a target system (server) and jumping from the gateway to log into the server. The configuration is simple, but the network configuration must be changed so that all access using a privileged ID can pass through the gateway, and as the server environment is distributed through public or private clouds and on-premises, the network configuration becomes more complex, making management more cumbersome.
In environments that use a public clouds, trying to control privileged access on gateway that are network boundaries poses many issues and is difficult to maintain control.
iDoperation, the go-to privileged access management tool iDoperation is available in hybrid configuration that combines client and gateway types.
iDoperation is a client-agent type privileged access management tool that enables granting of privileged IDs from the access source. Client-agent type tool is available in hybrid configuration that resolves a range of issues found in gateway type privileged access management tool, regardless of network configuration, and enables access control and acquires access log.
Moreover, depending on the customer operating environment, tool can be implemented through hybrid configuration combining the client-agent and gateway type tools, which would solve the five problems with gateway-type privileged access management tools.